Blood Sugar Levels After Meals – What’s Normal and What’s Not
Time to read 8 min
Time to read 8 min
Table of contents
It is essential to manage the blood sugar level and maintain normal glucose levels in the human body as it ensures the maintenance of, overall health, reflecting the body's ability to regulate glucose.
To manage the blood sugar level effectively, especially for diabetes management. Patients should monitor their sugar levels after meals and opt for methods like intermediate fasting, and a blood glucose test can further assist in managing their levels. to ensure they produce enough insulin . The blood sugar level after meal is known as postprandial blood glucose levels which is important as it reveal how the body is acting and managing the intake of carbohydrates. This can help to monitor and take control of the sugar level as there will be early signs of insulin resistance when measured.
In order to counter illnesses like diabetics, you should focus on the post-meal blood sugar levels that can prevent any future medical complications which can help with treating the disease based on patient immune system. Even if you are not diabetic, you should consider measuring blood sugar level post meal as it can help to predict and measure the sugar level fluctuations that will impact energy, mood, and long-term health.
In this article we will cover everything you need to know about the postprandial glucose and blood glucose levels. and why is it important for your health.
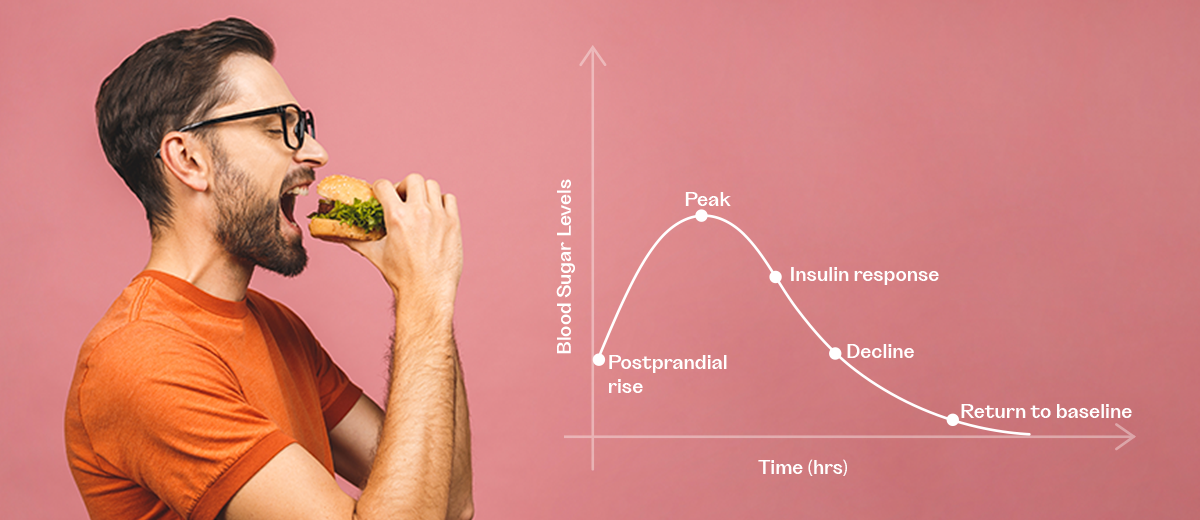
Postprandial blood sugar (PPBS) is the blood glucose levels that can be measured after eating a meal. The term postprandial contradicts after eating. The measurement of the blood sugar through a blood sample and glucose test should not be done after 8-12 hours of meal. To measure and ensure accurate reading, you should measure your sugar level after 2 hours of your meal, especially considering different foods consumed, and report results in mg dl.
PPBS is different from fasting glucose as it measures the baseline of the blood sugar when the body is not actively digesting food, which can help prevent heart disease and kidney disease, but also keep an eye on low blood sugar.
Meanwhile, the postprandial glucose displays the sugar level after consuming carbohydrates and how the sugar level rises, indicating high blood sugar, and when it returns to the baseline, affecting your energy levels.
The PPBS should be measured only under medical guidance from a healthcare professional, and a glucose test, as the expert suggests, should be conducted after a meal.
1 hour post-meal: You should check the initial spike in the blood sugar level.
2 hours post-meal: This is the best time to record the peak of the PPBS suggested by doctors.
3 hours post-meal: After 2 hours of the meal, you should check if the blood level is returning to the baseline.
4 hours post-meal: This can be considered as the case of fasting to measure your blood sugar.
The blood sugar level after a diabetes diagnosis should show the following measured scale of 140 mg dl to ensure the healthy functioning of the body, maintaining normal blood sugar levels considering other factors that can influence levels.
The reading varies for people with non-diabetics and diabetics. Below is a general range of blood sugar levels for eating adults.
1 hour after meal: the readings should be below 180 mg/dL
2 hours after a meal: The readings should drop down to the 140 mg/dL
3 hours after meal: The readings should measure 100 mg/dL or lower.
4 hours after a meal: This should show the lowest measurement of the blood sugar level, which ranges from 70–100 mg/dL.
According to the American diabetes association, these numbers can vary depending on a person’s immune age, metabolism, health conditions, and the presence of gestational diabetes, especially for older adults.
It is crucial to measure the blood glucose PPBS as it can help to ensure that your body is functioning correctly and plays a key role in preventing health issues. , as high blood sugar or low blood sugar can lead to various serious health problems, diabetes complications and health problems, and impact your overall wellbeing.
The PPBS shows how well your body can adapt or handle the glucose after having meals, indicating insulin sensitivity, and with regular monitoring of fasting blood sugar levels, you can prevent long-term medical complications, such as nerve damage, ensuring healthy well-being.
If there is a case of uncontrolled spikes in blood sugar level, it can risk various serious illnesses, including type 2 diabetes, even if it shows a fasting value later.
The blood sugar level often spikes after having your meal in the first 30–60 minutes of eating, largely influenced by your digestive system .
The Normal range of the PPBS is from <180 mg/dL for most adults. If the reading consistently shows higher than this value and goes beyond the target range due to high glycemic index foods , you should consider having medical attention.
This is the advised and most used period of tracking your blood sugar level, along with monitoring food portions, and the reading is accurate and reliable.
The normal range for the non diabetic is from <140 mg/dL and for diabetics <180 mg/dL, especially if you are physically active.
The blood sugar level will start to return to its baseline and show lower readings close to the fasting level, so the blood sugar level will typically be around 100 mg/dL or lower. If the reading shows higher than this value, then it means that your body is resisting insulin, and it is essential to stay hydrated.
With the fourth hour the levels will be of fasting levels and show a value of 70-100 70–100 mg/dL.
There are many factors responsible for higher post meal blood sugar, which may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease . Below are some factors mentioned as well as other health conditions that may contribute to higher post meal blood sugar :
If you are consuming meal that is high in glycemic and includes sugary snacks or white bread then there is a higher chance that your blood sugar will show higher spikes than complex carbs or fiber-rich meals.
Choose to add protein, fat and fibre in your meal to prevent the overdosing of carbohydrates.
Lack of physical activity can also impact the level of blood sugar as it can influence the spikes.
Being sensitive towards insulin can also lead to the sugar stay longer than normal that can raise the blood sugar level.
The timing of measuring the Blood sugar level should be after 1 and two hours after eating a meal as there are many guidelines and studies that suggest that it is the ideal time for a blood glucose test, and the spikes show the accurate measurement of the glucose tolerance of the body.
People with medical conditions or pregnant women results may vary from the non diabetic and might require more medical care.
If the postprandial glucose level is high consistently then it is time for you to take action and look out for medical help as it can indicate serious medical complications. The high postprandial glucose can indicate risks like:
Insulin resistance: The consistent high level of blood sugar shows that the body is insulin resistant and have prediabetes and type 2 diabetes.
Poor carbohydrate tolerance: The body is not able to absorb the carbohydrate which is leading to higher spikes.
If the level of PPBS is higher then it can impact your kidney and damage other cardiovascular and nerve system.
If there is a case of regular spike in blood sugar level after a meal then you should consider changing and adapting to your diet.
You can opt for foods which are low glycemic like Whole grains, legumes, non-starchy vegetables.
Do not take carbohydrates alone, always pair them with protein or other fiber to ensure better glucose absorption. Pair carbs with protein and fiber.
Do not overeat the carbohydrates as it can lead to unwanted spikes in blood sugar.
You can practice walking after having your meal for 10-15 minutes as it will help to lower down the blood sugar level.
If you consume healthy amount of water it can prevent the dehydration spike of blood sugar.
Choose to have medical attention or insulin if its recommended by your doctor.
Choosing to monitor the postprandial blood sugar and incorporating healthy fats into your diet can prove to be a healthy way to achieve blood sugar control, prevent any further medical complications and ensure your overall well-being.
The normal ranges for the non-diabetic should range below 140mg/dL after two hours of finishing their meal, while for those with diabetes mellitus, different ranges apply. If you consistently have high readings, you are advised to seek medical attention, as doctors can help you lower your sugar level to a baseline.
Thus, it is important to understand how your body responds after meals and by tracking the blood sugar levels and fasting blood sugar levels, you can make moderate changes to your lifestyle and diet, as research shows, to ensure a healthy lifespan.
This will reduce the chance of any long-term disease and provide better health benefits to your body, making a big difference in your overall health. choose medical attention if required.
The blood sugar level for non diabetic which ranges below 140mg/dL after two hours of eating can be considered normal meanwhile for diabetics the sugar level should be under 180 mg/dL.
The blood sugar level can be maintained through fasting if it is not high for a consistent period of time and does not require medical attention, ensuring it remains within the target range .
It is recommended by doctors and experts to measure your blood sugar 2 hours after having a meal as it can ensure accurate glucose result.
If your blood sugar reading is 200 then it is not a good sign as it can indicate that you are prone to diabetes or other serious medical condition. Take medical guidance with doctors if this is persistent.
**Medical Disclaimer: The following information is for educational purposes only. No information provided on this website, including text, graphics, and images, is intended as a substitute for professional medical advice. Please consult with your doctor about specific medical advice about your condition(s).