Vitamin D3 Foods for Vegetarians in India: Sources, Benefits & Deficiency Fixes
Time to read 9 min
Time to read 9 min
Table of contents
Vitamin D3 or Cholecalciferol is a crucial nutrient that supports overall health. Vitamin D3 is also known as the ‘Sunshine Vitamin’ because skin produces vitamin D when it comes in direct contact with sunlight. The key role is to help the body absorb essential nutrients, calcium, and phosphorus, which contribute to stronger bones and teeth.
Vitamin D3 supports muscle health, improves immunity and mood, and contributes to overall well-being. A vitamin D deficiency can cause fatigue, weak bones, low immunity, and mood changes. You can maintain healthy levels of vitamin D3 by getting adequate sunlight, consuming vitamin D3-containing foods, and taking supplements.
Cholecalciferol is the most effective and bioavailable form of vitamin D, which means it can be easily absorbed by the body as compared to other forms of vitamin D. It’s the natural form created by the skin itself and maintains healthy vitamin D levels in the body. It is the most preferred form that improves complete health.
When it comes to how to get vitamin D3, usually vegetarians struggle to meet their vitamin D3 needs, as there are limited options for plant-based sources. Most natural sources of this vital vitamin come from animal-based foods such as eggs and fish. Plant-based sources contain very little vitamin D; thus, fortified food options and vitamin D supplements can help maintain adequate vitamin D levels in the body.
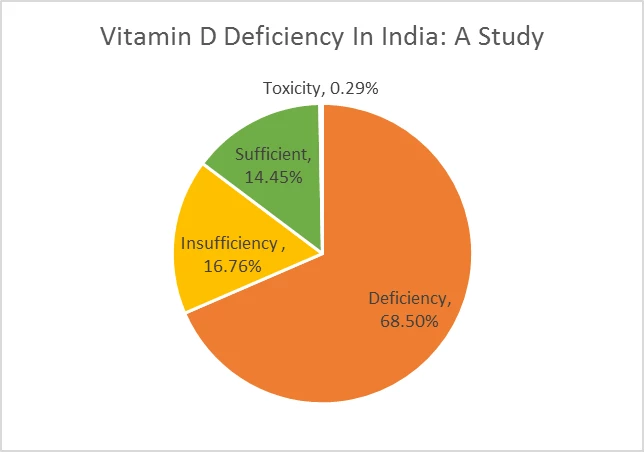
More than 80% Indians have an inadequate level of vitamin D or vitamin D deficiency. Here’s the pie chart demonstrating the global prevalence of vitamin D deficiency.
Vitamin D3 is formed by the skin itself when it is exposed to sunlight, and thus is considered the natural form. It can also be obtained from animal-based foods, including eggs, fish, and liver.
Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol) is different from vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol). Vitamin D3 can be obtained from sunlight and animal food sources, while vitamin D2 can be obtained from plant sources, particularly fungal sources such as mushrooms.
Vitamin D3 is a more efficient form of vitamin D and is better used by the body, which contributes to sufficient vitamin D level maintenance in the body for a longer period.
Both are closely related but not the same. The vitamins that allow calcium absorption in the body and maintain healthy bones are categorized under vitamin D. So, the main vitamin D and D3 is vitamin D3 is form of vitamin D.
When your skin comes in direct contact with sunlight, particularly the UVB rays, it naturally makes vitamin D3 using 7-dehydrocholesterol, a substance found in the skin. Then it is processed by certain body parts (liver and kidneys) to produce vitamin D that is actually used by the body.
Here’s the table to summarize the information you should know about Vitamin D3:
Characteristics |
Details |
Name |
Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol) |
Type |
Natural form produced by the skin through sunlight |
Prime sources |
Sunlight (UVB rays), eggs, fatty fish, liver, and fortified foods |
Key function |
Calcium and phosphorus absorption contribute to strong bones, teeth, and muscles. |
Secondary functions |
Better immunity prevents bone diseases and reduces fatigue. |
Daily Vitamin D requirement |
Daily vitamin D intake is 600-800 IU for adults |
Vitamin D insufficiency effects |
Fatigue, weak bones, bone diseases, low immunity, and muscle weakness. |
Risk of deficiency |
Vegetarians, elderly people, darker skin tone, people with no or limited sun exposure, and those living in polluted regions. |
Vitamin D3 has an important role in maintaining strong bones and body health. Here are the prime vitamin D uses in the body:
Vitamin D3 allows better absorption of calcium and phosphorus, which is vital for building and maintaining healthy bones and teeth. It helps prevent bone fractures, weak bones, and medical conditions such as osteoporosis and rickets.
It supports the immune system, allowing the body to combat infections more efficiently. Vitamin D3 helps improve muscle strength and function, supports muscle coordination, and prevents the risk of falls and weakness.
Vitamin D improves brain health and mood, preventing fatigue, stress, and the risk of depression.
Vegetarians and individuals who mostly stay indoors are more prone to vitamin D3 deficiency as they have limited dietary sources of it, and they are not well exposed to the sunlight. Severe vitamin D deficiency due to inadequate vitamin D intake can cause hair thinning, hair loss, and frequent illnesses.
Vitamin D3 is mainly obtained from animal-based foods such as eggs, liver, and fatty fish, so vegetarian people usually miss out on getting this vitamin. Indoor workers do not get exposed to sunlight as they spend most of their time indoors, so their skin can not make vitamin D3, causing lower vitamin D levels.
Both of these groups need fortified foods and vitamin D supplements to obtain and maintain adequate vitamin D levels in the body.
Weak bones due to poor calcium absorption
Muscle cramps and weak muscles
Fatigue and tiredness
Stress and depression
Frequent illnesses and infections
Dental concerns
Fractures and bone distortions
The best vitamin D3 foods are fortified foods and animal-based foods. The richest sources of vitamin D3 include fatty fish such as tuna, sardines, mackerel, and salmon. Other good sources are beef liver, cod liver oil, or egg yolks.
For vegetarians, fortified foods including milk, orange juice, and breakfast cereals can help enhance vitamin D consumption.
Vitamin D3 is primarily found in animal-based foods but can be derived from vegetarian fortified sources. Here’s the list of natural vitamin D foods:
Fatty fish (tuna, herring, sardines, mackerel, and salmon.
Cod liver oil (the richest natural source)
Egg yolks
Beef liver
Cheese
Ghee and butter
Fortified cereals
Fortified milk
UV-exposed mushrooms
Here’s the list of the best vegetarian D3-rich foods:
Fortified dairy products: Fortified milk, curd, and cheese spreads (Nestle, Mother Dairy, and Amul Taaza).
Fortified plant-based milk: Fortified almond milk, soy milk, and oat milk (great for lactose-intolerant people (Raw Pressery almond and sofit soy).
Fortified cereals and juices: Corn flakes plus, Kellogg’s Special K, Quaker oats, orange juice, and some other packaged juices have added vitamin D3.
UV-Exposed mushrooms: Sun-exposed shiitake, button, and oyster mushrooms naturally contain vitamin D.
Fortified oils and ghee: Some cooking oils are fortified with vitamin D and are considerable vitamin D3-rich foods for vegetarians.
Fruits don’t contain vitamin D3; however, some fruits help vitamin D absorption. Fruits are not a direct source of vitamin D3, but fortified juices such as orange juice and fruits containing healthy fats, vitamin C, and magnesium actually support the use of vitamin D3 in the body.
The fruits that support the efficient use of vitamin D3 include oranges, mangoes, bananas, kiwis, lemons, and avocados.
Wondering how to increase vitamin D3 levels in the body? Here’s the list of foods to increase vitamin D3:
Vitamin D3 is a fat-soluble vitamin, which means it requires healthy fats to be well absorbed in the body. Combining it with the suitable foods can efficiently improve how well your body uses it.
Vitamin D foods paired with healthy fats such as ghee and olive oil
Vitamin D foods paired with magnesium-rich foods, such as nuts and seeds
When it comes to the most effective natural source of vitamin D3, it is the sun exposure. 15-20 minutes of direct sunlight exposure can produce up to 1000 IU of vitamin D. Sunlight exposure, especially UVB rays, allows natural production of vitamin D that is used by the body to support muscle and bone health and immunity. Vitamin D3-rich foods and vitamin D supplements can help meet the requirements in body.
As vitamin D3 is mainly found in animal-based foods, vegetarians and vegans usually do not get enough vitamin D and struggle to meet their vitamin D3 needs. They can maintain healthy D3 levels in their body, considering lichen-based vitamin D supplementation that is completely plant-driven.
Lichen is an organism that naturally produces vitamin D3 just like human skin, making it an excellent alternative to animal-based products.
Check your Vitamin D production in your body through the Vitamin D test at Mydiagnostics.
Check out the table mentioned below to get a clearer picture of vitamin D Sources:
Source |
Examples |
Benefits |
Fatty fish |
Salmon, sardines, trout, tuna, herring, mackerel |
Best natural source and highly bioavailable |
Animal-based foods |
Cheese, butter, beef liver, egg yolks |
Moderate source and pair with healthy fats for enhanced absorption |
Fortified food products |
Fortified milk, curd, orange juice, cereals, soy milk, almond milk, oat milk |
Suitable for indoor workers and vegetarians |
Plant-based sources |
Sun-exposed mushrooms such as oyster shiitake |
Improve complete vitamin D levels in the body |
Vegan supplements |
Lichen-based supplements |
Excellent option for vegans and vegetarians |
Sunlight |
Morning and evening sun exposure |
The natural and most efficient source |
Vitamin D3 or Cholecalciferol is a crucial nutrient for stronger muscles, bones, and teeth. It allows better absorption of calcium and phosphorus in the body. Vitamin D3 also helps maintain immune health and mood regulation, and contributes to overall well-being.
The human body naturally produces vitamin D as it is exposed to direct sunlight, and it is also found in certain plant-based foods and supplements. Vitamin D3 deficiency is associated with fatigue, weak bones, fractures, mood changes, and poor immunity.
Vegetarians and vegans can fulfil their body’s vitamin D requirements by considering a combination of sunlight, fortified foods and dairy products, and vegan supplementation. Lichen-based supplements are an effective option for vegetarians.
The foods that contain the highest vitamin D3 include fatty fish, UV-exposed mushrooms, and fortified foods.
UV-exposed mushrooms, fortified milk and cheese, fortified cereals, and soy milk.
Vitamin D3 is the more natural form of vitamin D that is produced by the body when it comes in contact with direct sunlight.
Spend at least 15 minutes in the sunlight in the morning, consume fortified foods, fortified dairy products, and mushrooms.
Fruits do not contain vitamin D, but certain fruits, such as oranges and avocados, support better absorption of vitamin D.
Healthy fats, including ghee, seeds, and nuts, and magnesium found in lentils and leafy greens, allow better absorption of vitamin D3.
Vitamin D is mainly found in animal-based foods such as eggs and fatty fish. Vegetarians find it difficult to meet adequate amounts naturally. Vegetarians can get vitamin D by considering sunlight-exposed mushrooms, fortified dairy products, fortified vitamin D-rich foods, and vegan D3 supplementation as recommended by health professionals.
Daily vitamin D3 requirement depends on the age, sunlight exposure, and lifestyle of an individual. Typically daily requirement for adults is 600-800 IU, while people with vitamin D deficiency may require higher doses as recommended by a healthcare provider.
***Medical Disclaimer - The following information is for educational purposes only. No information provided on this website, including text, graphics, and images, is intended as a substitute for professional medical advice. Please consult with your doctor about specific medical advice about your condition(s).